Category: Hazardous and Solid Waste
Voluntary Waste Reduction and P2 Programs Still Going Strong
Common Violations of Universal Waste Regulations
Beware of ‘Legacy’ Mercury-Containing Equipment
E-Waste Recycling Comes of Age
Managing E-Waste with the ‘Three Rs’
PCB Marking Requirements
Each of the following items must be marked with the large label as illustrated in this section. Where the large PCB mark is specified, but the PCB article or PCB equipment is too small to accommodate the smallest permissible size of the large mark, the small PCB mark may be used instead of the large […]
Lamp Recycler Fined for PCB Violations
According to EPA, the facility is permitted under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) to manage and store PCB wastes. Separate permits allow the facility to recycle fluorescent lamps and ballasts, batteries, electronic wastes, and mercury devices. The facility also manages non-PCB ballasts, phosphorous powders, aerosol cans, and mercury-containing wastes. The company operates facilities in […]
Bill Halts Guidance on ‘Federally Regulated Waters’
Following are key points made in the draft guidance in three critical areas–significant nexus, tributaries, and adjacent wetlands. Significant Nexus To evaluate the presence or absence of a significant nexus, the agencies intend, as a general matter, to consider: • Waters similarly situated with waters of the same resource type, specifically tributaries, adjacent wetlands, or […]
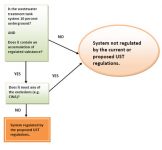
EPA’s Proposed UST Rules – Wastewater Treatment Tanks
What is a wastewater treatment tank system? A wastewater treatment tank system is designed to receive and treat influent wastewater through physical, chemical, or biological methods. That means if wastewater flows through a system and is treated in some way, then that system is considered a wastewater treatment tank system. For example, oil-water separators treat […]