Since 1919, the hard hat has been the most iconic symbol of worker safety. But despite more than 6 million hard hats and safety helmets sold each year, over 18,000 still suffered traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) in 2019 (BLS data).
And while hard hat technology has evolved tremendously over the last century, there’s one thing that really hasn’t—a one-track focus on protection from direct, linear impacts. Though incredibly important, this focus has neglected the TBI-causing rotational forces that often result from more common angled impacts.
DIRECT IMPACTS VS. ANGLED IMPACTS
To understand what an angled impact is, we first need to understand direct impact.
A direct impact is, well, exactly that—a square, dead center hit to the top or sides of the head. When a perfect direct impact occurs, there is very little rotational force on the brain (more on that in a bit). Which is all fine and dandy except for that when an object, floor or beam comes trajecting toward your brain, it’s not going to give you the common courtesy of adjusting its path to hit you square on.
More frequently, the object is going to strike your head at an angled impact—introducing rapid rotational forces against the brain’s center of gravity. Unlike a concentrated compression caused by a single direct impact, rotational forces cause the brain to twist or pull in multiple directions. These shifts and rotations can cause a tearing of nerve fibers, a side effect known scientifically as brain shear (or brain jiggle, as we like to call it).
And brain jiggle = bad.
WHY ARE ANGLED IMPACTS SO DANGEROUS?
Due to the pulling, stretching and overall bad juju of brain shear, angled impacts are actually more likely to result in traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) than direct impacts. What makes things even more concerning is the frequency at which brain shear-inducing incidents occur on the worksite. Falls, which are more likely to result in angled impact, are the most common worksite accident—and also the most common incident to result in a TBI.
As anyone who has followed the evolving saga of head trauma in professional sports knows, the effects of TBIs can be delayed, long-lasting and life-changing. In 2019 alone, there were 61,000 TBI-related deaths in the United States.
TBIs resulting from brain shear are known as closed brain injuries. Unlike an open brain injury, these occur without breaking the skull. The type of closed brain injury that most frequently occurs as a result of an angled impact is Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI). DAI is the shearing of the brain’s long connecting nerve fibers (axons) that happen to the brain as it shifts and rotates. “Diffuse” refers to how the resulting dysfunction spreads to a widespread area throughout the brain. Often, these tears are microscopic and cannot be seen on CT or MRI scans.
A concussion is considered to be a mild form of DAI, resulting in symptoms such as headache, dizziness or memory loss. While symptoms of concussions and more severe DAIs can certainly show immediately after the impact, they often evolve in the following hours, days or weeks.
WHAT’S BEING DONE TO PROTECT WORKERS FROM ANGLED IMPACTS?
Currently, both North American Hard Hat Standards (ANSI Z89.1 and CSA Z94.1) only test for direct, linear impacts. Type 1 hard hats are approved for top of head, with Type II approved for top, front, back and sides.
To meet ANSI Z89.1 as well as European standards, a hard hat or safety helmet must pass a force transmission test. In this test, the hat or helmet is placed on a dummy and hit squarely with an 8lb (3.6kg) impactor from the top. If testing for Type II, it will also be hit from the front, back and sides.
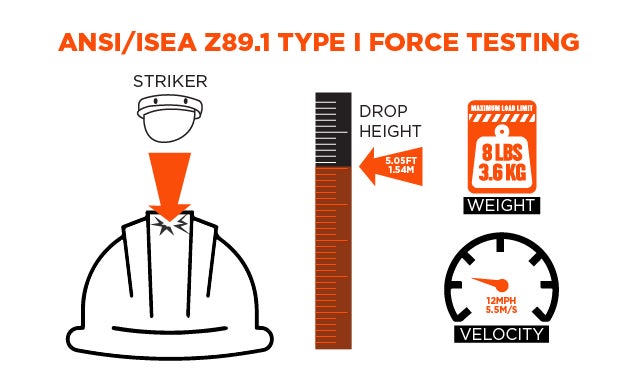 This method determines individual maximum force readings based on various impact velocities. To be approved for the worksite, the hat or helmet cannot transmit over 4,450 newtons (1,000 pound-force).
This method determines individual maximum force readings based on various impact velocities. To be approved for the worksite, the hat or helmet cannot transmit over 4,450 newtons (1,000 pound-force).
Certainly, direct impact testing is incredibly important to worker safety. And yet, the limitations of this widely used method do not adequately measure rotational forces caused by angled impacts. And considering the TBI-causing risk of rotational forces, it’s clear that something’s missing. That’s where Mips® comes in…
HOW MIPS® TECHNOLOGY REDUCES EFFECT OF ROTATIONAL FORCES
In 1996, Swedish neurosurgeon Hans von Holst began exploring the relationship between brain injuries and helmet construction. Upon recognizing helmets were inadequately protecting against rotational impacts, von Holst teamed up with researcher Peter Halldin to engineer a solution.
Their efforts resulted in the creation of a multi-directional impact protection system now known more simply as Mips®. This technology is built around the discovery that relative motion between low friction layers reduces the effect of rotational force. By integrating a sliding layer into helmets, von Holst and Halldin found a way to redirect the force of rotational impacts that would otherwise be transferred to the head.
To test effectiveness, Mips® helmet test lab includes four testing machines designed to mimic real-world impact scenarios. Of the many comprehensive and helmet-specific tests conducted in the lab, Mips has found a vertical drop onto an angled surface to be the most simple and robust method for determining reduction of rotational force.
Initially focused on the recreational space with bike and ski helmets, Mips is now expanding into the industrial space with collaborations such as the Skullerz Safety Helmet.
Unlike traditional hard hats, Skullerz Safety Helmets with Mips have the Elevate Safety System integrated directly into the suspension to protect workers from overlooked angled impacts.
Think safety helmets are just for tower climbers and arborists? Think again. The enhanced impact protection provided by the safety helmet’s compact shell has them trending as an alternative to hard hats on a variety of industrial worksites.
 ELEVATE YOUR HEAD PROTECTION WITH SKULLERZ SAFETY HELMETS + MIPS TECHNOLOGY >>
ELEVATE YOUR HEAD PROTECTION WITH SKULLERZ SAFETY HELMETS + MIPS TECHNOLOGY >>
